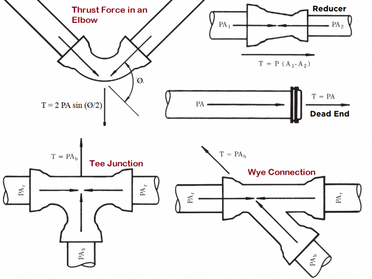
A thrust block is a structural component that is used to transmit the thrust force of a rotating shaft to the surrounding structure. It is typically used in machinery and equipment that has a high-thrust load, such as pumps, compressors, and turbines. The design of a thrust block involves calculating the expected thrust load and selecting materials and a configuration that can withstand that load while also minimizing weight and cost. The design of thrust block also need to consider the alignment of the shaft and the surrounding structure and the ability to dissipate heat generated by the thrust load.
Thrust Block Design
Thrust block design is the process of designing a structural component that can transmit the thrust force of a rotating shaft to the surrounding structure. The thrust force is a force that acts in the direction of the shaft’s rotation, and it is generated by the rotation of the shaft and the load it is carrying. The thrust force needs to be transmitted to the surrounding structure in order to prevent damage to the shaft and the equipment it is connected to.
The design process begins by determining the expected thrust load that the thrust block will need to withstand. This involves calculating the torque and speed of the shaft, as well as the load that the shaft is carrying. The next step is to select materials and a configuration that can withstand the expected thrust load while also minimizing weight and cost. Common materials used in thrust block design include steel, cast iron, and bronze.
The design of the thrust block also needs to take into account the alignment of the shaft and the surrounding structure. The thrust block must be able to support the shaft in the correct position, and it must be able to transmit the thrust force to the surrounding structure without introducing any misalignment or binding.

The design also need to consider the dissipation of heat generated by the thrust load. If the heat generated by the thrust load is not dissipated properly, it can cause damage to the thrust block and the surrounding structure. This can be achieved by adding cooling systems or by selecting materials with high thermal conductivity.
Finally, the design must also consider the safety, reliability, and maintenance of the thrust block. This includes ensuring that the thrust block is easy to access and maintain, and that it is designed to prevent failure or malfunction.
Overall, thrust block design is an important aspect of machinery and equipment design, and it requires a thorough understanding of the loads and forces involved, as well as the properties of the materials used.
One important aspect is the design of the bearings that support the shaft. The thrust block must be able to support the shaft in the correct position, and it must be able to transmit the thrust force to the surrounding structure without introducing any misalignment or binding. This is achieved by using bearings that are designed for high thrust loads. The bearings can be either roller or journal bearings. The choice of bearings will depend on the specific requirements of the application, such as the shaft size, speed, and load.
Another important aspect of thrust block design is the need to accommodate for any axial movement of the shaft. This can be caused by thermal expansion, vibration, or other factors. The thrust block must be able to accommodate this movement without causing damage to the shaft or the surrounding structure. This can be achieved by using flexible couplings, or by designing the thrust block with a certain degree of flexibility.
Another important consideration is the need to provide an effective seal between the shaft and the thrust block. This is to prevent the ingress of foreign materials, such as dust, water, or other contaminants that can cause damage to the bearings or the shaft. This can be achieved by using sealant or by using mechanical seals.
Finally, it is important to consider the ease of maintenance of the thrust block. This includes ensuring that the thrust block is easy to access and maintain, and that it is designed to prevent failure or malfunction. It is important to have easy access to the bearings, seals, and other components of the thrust block for maintenance, inspection, and replacement as required.
Working of a Thrust Block in Pipelines
In pipelines, a thrust block is used to transmit the thrust force of a pump or compressor to the surrounding structure. The thrust force is a force that acts in the direction of the shaft’s rotation, and it is generated by the rotation of the shaft and the load it is carrying. The thrust force needs to be transmitted to the surrounding structure in order to prevent damage to the shaft and the equipment it is connected to.
The thrust block is typically located at the discharge end of the pump or compressor, and it is usually made of concrete or other heavy materials that can withstand the high thrust loads. The thrust block is designed to accommodate the movement of the shaft caused by thermal expansion or other factors. This can be achieved by using flexible couplings, or by designing the thrust block with a certain degree of flexibility.
The thrust block also includes bearings that support the shaft, and seals that prevent the ingress of foreign materials. The bearings used in thrust blocks for pipelines are typically journal bearings. The seals used are typically mechanical seals.
The thrust block also includes a system for dissipating the heat generated by the thrust load. This can be achieved by adding cooling systems or by selecting materials with high thermal conductivity.
The design of the thrust block also needs to take into account the alignment of the shaft and the surrounding structure. The thrust block must be able to support the shaft in the correct position, and it must be able to transmit the thrust force to the surrounding structure without introducing any misalignment or binding.
It is important to properly design and maintain the thrust block in pipelines to ensure the longevity of the equipment and to prevent failure or malfunction.
Applications of Thrust Block Design
Thrust block design is used in a variety of applications where a high-thrust load is present. Some of the most common applications include:
- Pumps: Pumps generate high thrust loads due to the rotation of the impeller, which can cause damage to the shaft and the surrounding structure if not properly supported. These blocks are used to transmit the thrust force to the surrounding structure, and to support the shaft in the correct position.
- Compressors: Compressors generate high thrust loads due to the rotation of the compressor rotor, which can cause damage to the shaft and the surrounding structure if not properly supported. These blocks are used to transmit the thrust force to the surrounding structure, and to support the shaft in the correct position.
- Turbines: Turbines generate high thrust loads due to the rotation of the turbine rotor, which can cause damage to the shaft and the surrounding structure if not properly supported. These blocks are used to transmit the thrust force to the surrounding structure, and to support the shaft in the correct position.
- Gearboxes: Gearboxes generate high thrust loads due to the rotation of the gears, which can cause damage to the shaft and the surrounding structure if not properly supported. These blocks are used to transmit the thrust force to the surrounding structure, and to support the shaft in the correct position.
- Pipelines: Pumps and compressors in pipelines generate high thrust loads due to the rotation of the impeller or compressor rotor, which can cause damage to the shaft and the surrounding structure if not properly supported. These blocks are used to transmit the thrust force to the surrounding structure, and to support the shaft in the correct position.
- Marine: Marine propulsion systems like propellers generate high thrust loads which can cause damage to the shaft and the surrounding structure if not properly supported. They are used to transmit the thrust force to the surrounding structure, and to support the shaft in the correct position.
These are some of the most common applications of thrust block but it can also be used in other industries like wind turbines, heavy machinery and conveyors. The key is that wherever there is a high-thrust load, these are needed to transmit the thrust force to the surrounding structure and to support the shaft in the correct position.
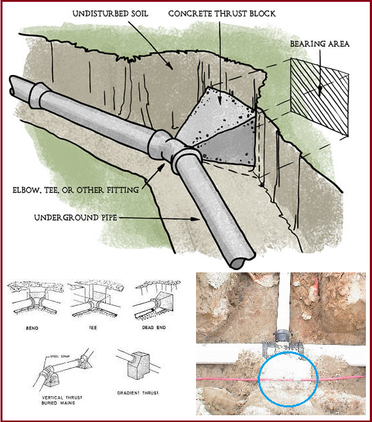
Advantages and Disadvantages of Thrust Block Design
These are used in piping systems to prevent the pipe from moving in the axial direction, or along its own axis.
Advantages of thrust block design include:
- They provide a secure and reliable means of preventing pipe movement, which can help to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the piping system.
- They are relatively simple and inexpensive to design, fabricate, and install.
- They can be used in a wide range of applications, including both low- and high-pressure systems.
Disadvantages of thrust block design include:
- They can be difficult to access and maintain, which can make it harder to diagnose and repair problems with the piping system.
- They can be bulky and take up a lot of space, which can be an issue in tight or confined areas.
- They may not be suitable for certain types of piping systems, such as those that require frequent adjustments or realignments.
- They can be affected by corrosion and erosion over time, which can reduce their effectiveness and lead to leaks or other problems with the piping system.
Thrust blocks are relatively simple and inexpensive to design, fabricate, and install. They provide a secure and reliable means of preventing pipe movement. On the other hand, they can be difficult to access and maintain, they can be bulky and take up a lot of space, they may not be suitable for certain types of piping systems, and they can be affected by corrosion and erosion over time.