What is Viscosity? Factors, Newton’s Law, and Importance of Viscosity in Various Industries
Viscosity refers to a property of fluids that characterizes their resistance to flow and determines their thickness. This property is determined by the internal friction within a fluid that acts to oppose the relative motion of its different layers. Fluids…
Stud Bolt : Types, Selection, Materials, and Standards of Stud-Bolt – A Detailed Account its Importance
A stud bolt is a specialized fastener utilized in a variety of high-pressure applications, including pipelines, pressure vessels, and related equipment. It is composed of a threaded rod and two heavy hex nuts, as well as a flat or square…
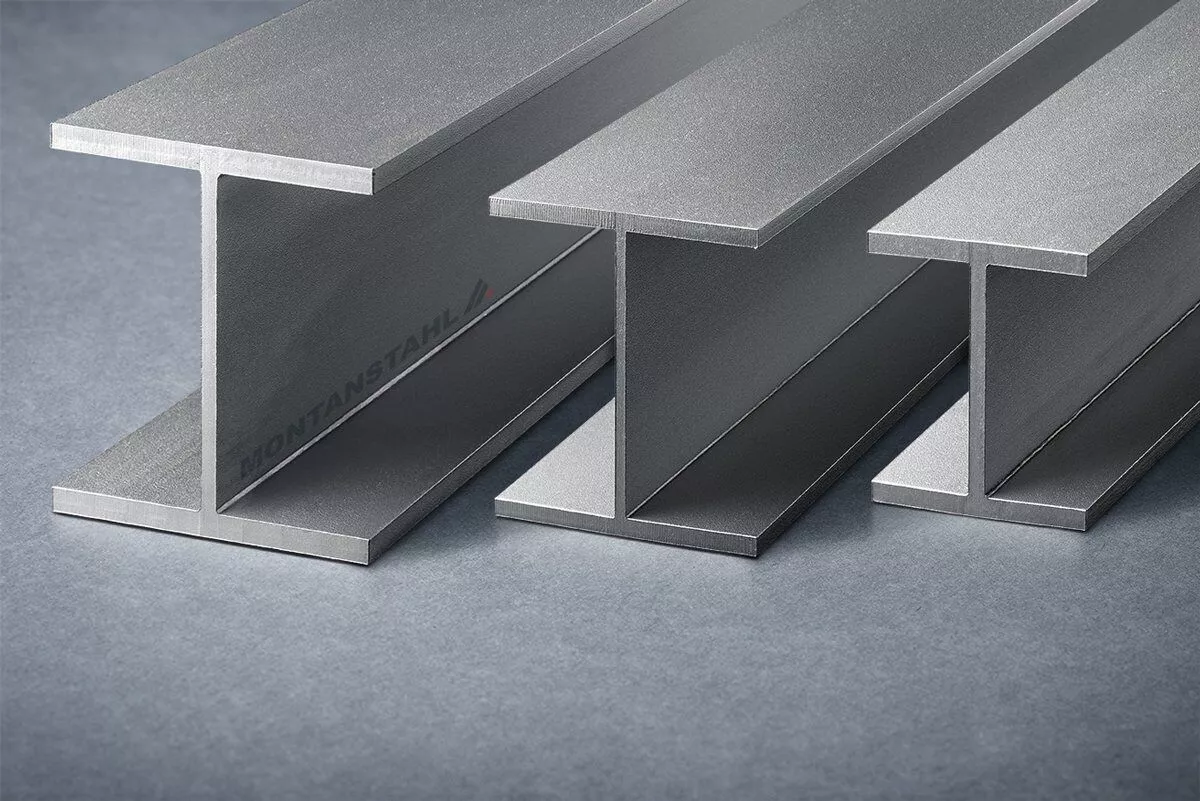
H-beam vs I-beam : Features, Similarities, Differences – A Precise and Informative Comparative Study
H-beams and I-beams are both types of structural steel commonly used in construction. The main difference between the two lies in their shape, with the H-beam having a wider flange (the horizontal section) compared to the I-beam. The flange of…
What is Monel? Properties, Applications, Grades, Advantages, Disadvantages
Monel alloys were first introduced by the International Nickel Company (INCO) in the early 1900s and are named after the company’s president, Ambrose Monell. These alloys are known for their exceptional resistance to corrosion, especially in saltwater, making them a…
Cast Iron vs Cast Steel: How to identify Cast Iron and Steel
Cast iron and cast steel are both types of cast metals that are produced by pouring liquid metal into molds. Cast iron is an iron-carbon alloy that typically contains 2-4% carbon, 1-3% silicon, and small amounts of other elements. It…
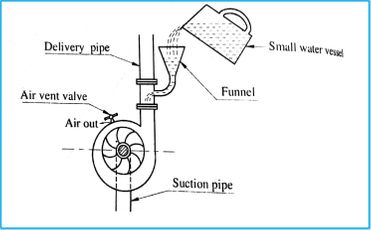
What is Pump Priming and Why it is Required?
Pump priming refers to the initial injection of government funds into an economy in order to stimulate economic activity and promote growth. This can take the form of infrastructure projects, tax cuts, or increased government spending on social welfare programs….
Most Common Types of Steel | Grades, Manufacturing of Steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon, along with small amounts of other elements. The carbon content in steel varies from less than 0.01% to around 2%, depending on the type of steel. The most common types of steel…
A36 Steel | Composition, Applications, and Properties of ASTM A36 Steel
A36 steel is a low carbon steel that is commonly used in construction and other heavy industries. It is made up of iron and carbon, with the carbon content typically ranging from 0.25% to 0.29% by weight. This steel has…
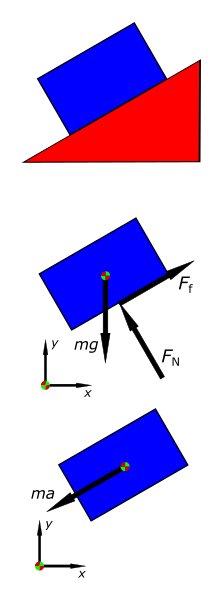
Free Body Diagram: Definition, Purpose, Examples, Steps
A free body diagram (FBD) is a pictorial representation of an object and the forces acting on it. It is used to simplify and analyze the forces acting on a body in order to determine the net force and the…
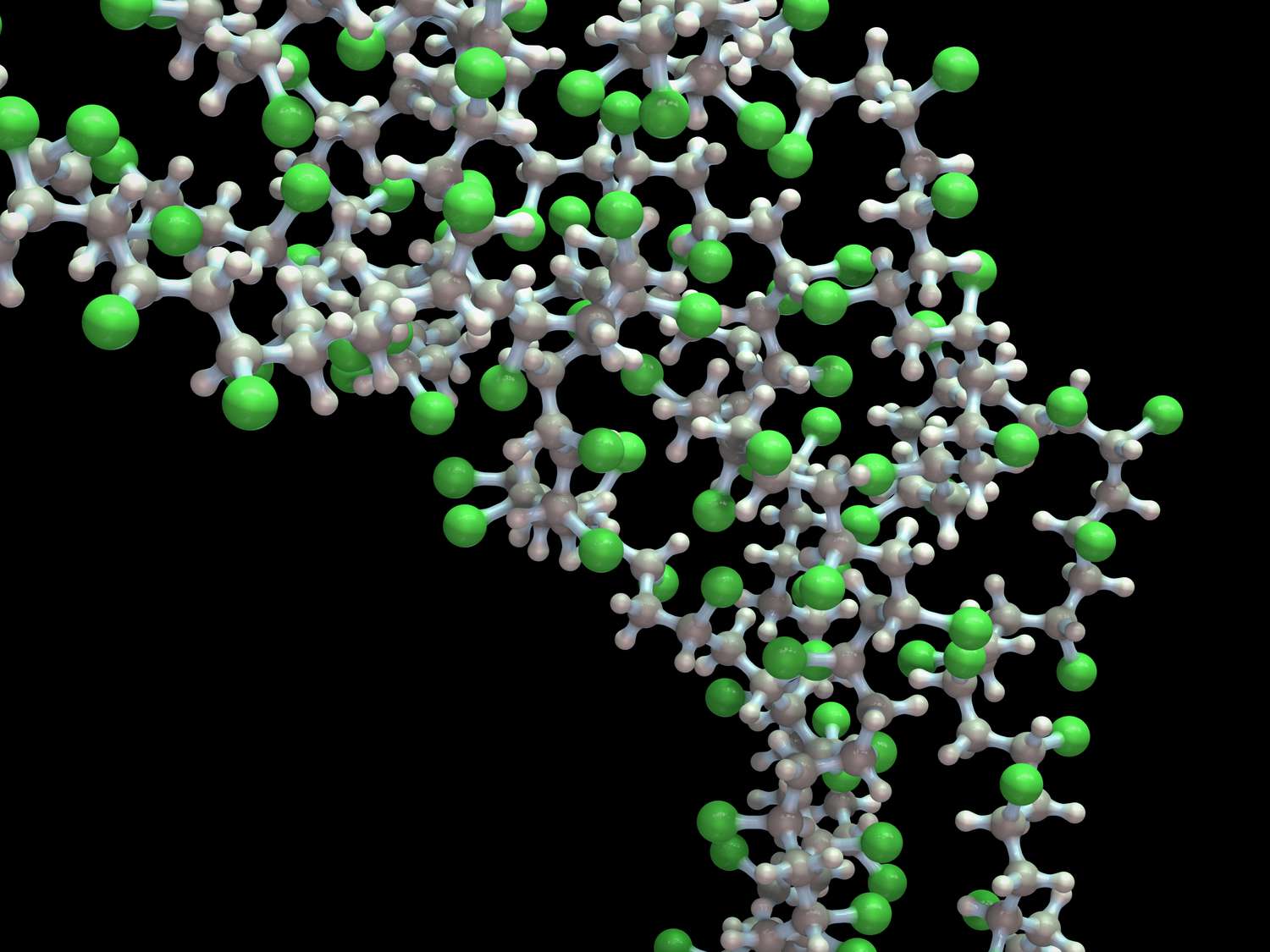
What are Polymers? Their Definition, Types, Examples, Uses, Working.
Polymers are large molecules made up of repeating units called monomers. These molecules can have a wide range of properties, depending on the type of monomers used and the way the polymer is formed. Some common examples of polymers include…