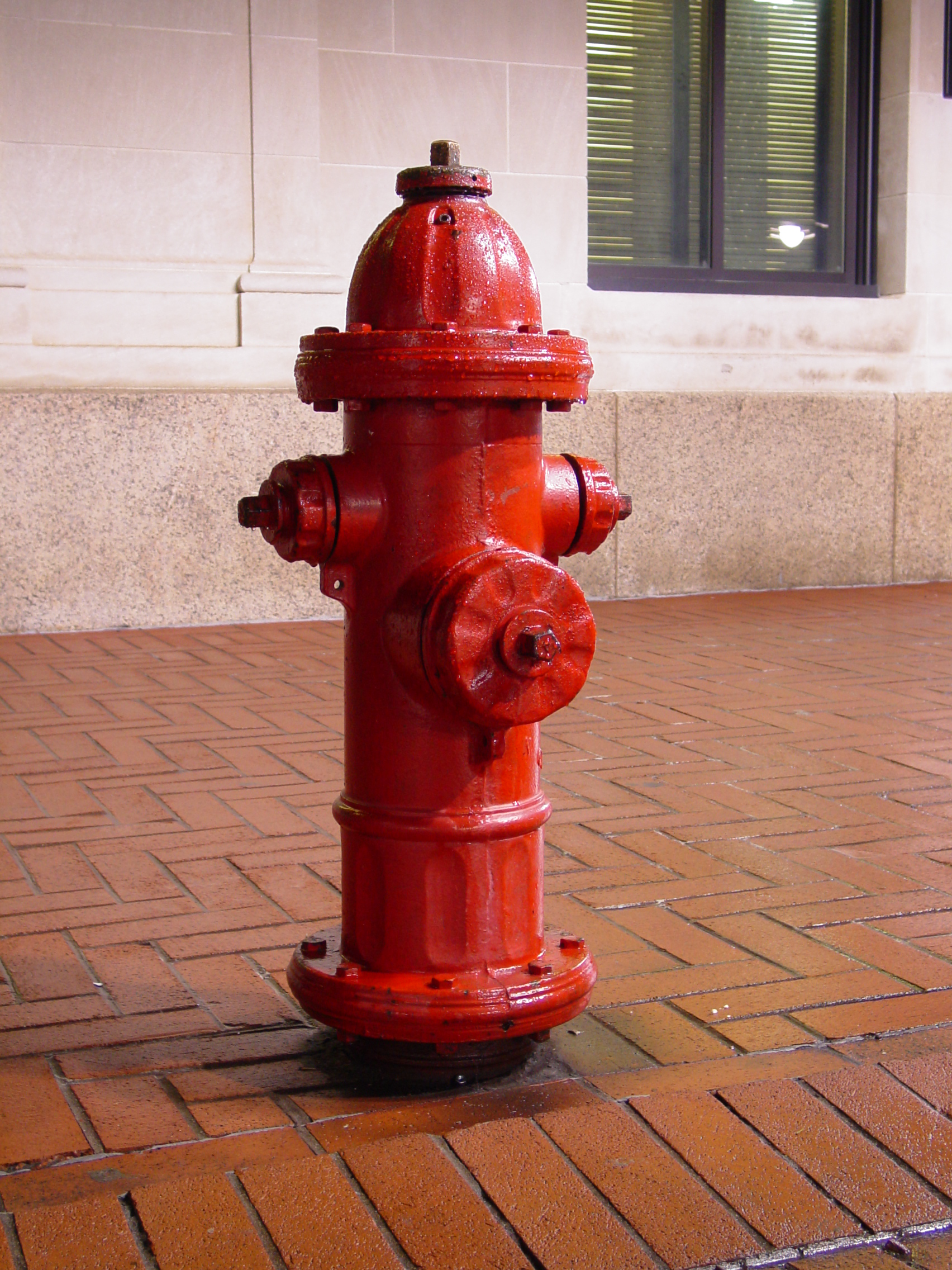
A fire hydrant is a device that is used to pump water from a municipal water supply system to extinguish fires. It typically consists of a vertical metal pipe with a valve at the base, which can be opened to release water under pressure, and a series of connections and outlets for attaching hoses. Fire hydrants are typically located on public streets and are available for use by fire departments in case of emergency.
In addition to their use in firefighting, fire hydrants also have other important uses. They can be used to provide water for construction and street-cleaning purposes, and they can also be used to flush out water mains and fire-protection systems. Some municipalities also use fire hydrants to provide water for irrigation and other non-firefighting purposes.
Fire hydrants must be regularly inspected, tested, and maintained to ensure that they are in good working condition and capable of providing an adequate water supply in case of fire. This includes regular flushing to remove sediment, testing of valves and outlets, and checking for leaks or other damage.
Overall fire hydrant is an essential piece of firefighting equipment that provides a reliable source of water for extinguishing fires and is an important part of a community’s fire protection infrastructure.

Working of Fire Hydrants
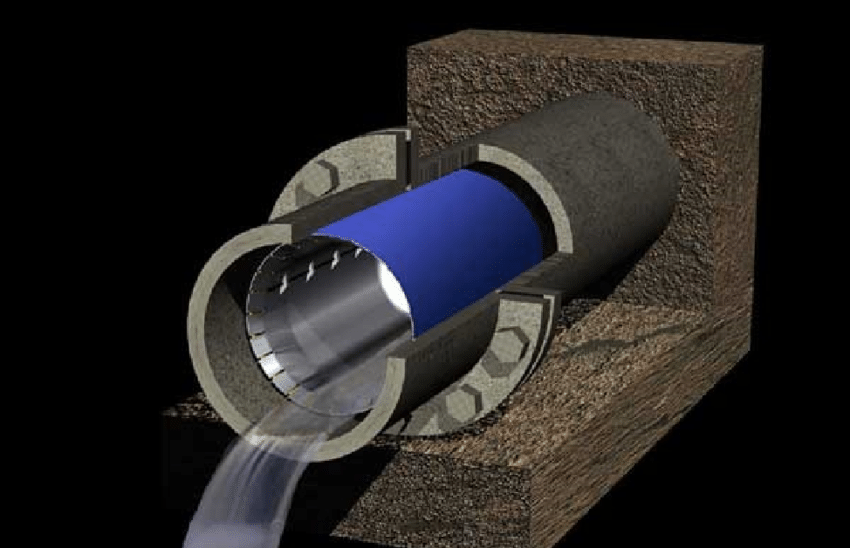
A fire hydrant is a device that is connected to a pressurized water supply system, such as a municipal water supply. The hydrant consists of a vertical metal pipe, called the “stem,” which is connected to the water supply system, and a valve at the base, which can be opened to release water under pressure. The top of the hydrant typically has a series of connections and outlets, called “ports,” where hoses can be attached.
When a fire breaks out, firefighters use a specialized tool called a “hydrant wrench” to open the valve on the hydrant. This allows water to flow out of the hydrant and through the attached hoses at a high pressure. The water is then used to extinguish the fire.
The working of these hydrants is based on the principle of “water hammer” effect. As the valve is opened, the water pressure in the hydrant drops suddenly, which causes the water to flow into the hydrant with a high velocity. As the water flows into the hydrant, it creates a pressure wave that travels upstream to the water main. This pressure wave causes the water in the main to flow into the hydrant at a high velocity, which helps to increase the water pressure in the hydrant.
It’s important to note that these should only be operated by trained professionals, as they can be dangerous if not used properly. Tampering with or vandalizing a these hydrant can also cause damage to the hydrant and the surrounding area, as well as interfere with firefighting efforts.
Purpose of Fire Hydrants
The primary purpose of these are is to provide a reliable source of water for extinguishing fires in urban areas. Firefighters can attach hoses to the outlets on the hydrant and use the water to extinguish the fire, which is crucial in urban areas where there are many buildings and structures that can catch fire. The water pressure provided by the fire hydrant allows firefighters to direct large amounts of water at a fire, which helps to extinguish it quickly and prevent it from spreading.
They also have other important uses. They can be used to provide water for construction and street-cleaning purposes, and they can also be used to flush out water mains and fire-protection systems. Some municipalities also use fire hydrants to provide water for irrigation and other non-firefighting purposes.

Fire hydrants are also used for test and maintenance purposes, for example, for testing the flow and pressure of the water supply system, and for flushing out the water mains to remove sediment and debris.
Overall, these hydrants are an essential part of a community’s fire protection infrastructure and play a vital role in ensuring public safety by providing a reliable source of water for extinguishing fires.
Types of Fire Hydrants
There are several types of fire hydrants, each designed for specific uses and environments. The most common types of fire hydrants include:
- Wet barrel hydrant: This is the most common type of hydrant and is used in most urban areas. It is designed to be used with a pressurized water supply system and has a valve at the base that can be opened to release water under pressure. The top of the hydrant typically has several outlets, or “ports,” where hoses can be attached.
- Dry barrel hydrant: This type of hydrant is used in areas where the water supply is not pressurized, such as in rural areas. It has a valve at the top of the hydrant that can be opened to release water into the hydrant, which can then be pumped out using a fire truck’s pump.
- Underground fire hydrant: This type of hydrant is buried underground and is typically used in areas where there is limited space above ground, such as in densely populated urban areas. They have a valve at the top that can be opened to release water, and hoses can be attached to the ports on the top of the hydrant.
- Pillar hydrant: This type of hydrant is designed for use in areas where the water supply is pressurized, typically in industrial areas. They have a valve at the base of the hydrant that can be opened to release water under pressure, and hoses can be attached to the ports on the top of the hydrant.
- Dry standpipe hydrant: This type of hydrant is designed to connect to a dry standpipe system, which is typically found in buildings. It is used to supply water to the standpipe system, which can then be used by firefighters to extinguish fires in the building.
- Monitor hydrant: This type of hydrant has a monitor, or nozzle, attached to it, which can be used to direct a powerful stream of water at a fire. They are typically used in industrial and commercial settings, such as airports and ports.
Each type of fire hydrant has its own set of advantages and disadvantages and is suited for specific situations and environments. Firefighters and fire departments are trained to use and operate all types of fire hydrants to ensure they can provide adequate water supply in case of emergency.

Components of Fire Hydrant System
A fire hydrant system typically includes the following components:
- Fire Hydrants: These are the visible components of the system that are located on public streets and are available for use by fire departments in case of emergency. They consist of a vertical metal pipe with a valve at the base that can be opened to release water under pressure, and a series of connections and outlets for attaching hoses.
- Water Supply: The fire hydrant system is connected to a pressurized water supply, such as a municipal water supply or a private well. This is the source of water that is used to extinguish fires.
- Valves: The valves are an important component of the system as they control the flow of water from the supply to the hydrant. These valves are typically located in underground vaults or in above-ground valve boxes.
- Pipes: The pipes are used to transport water from the supply to the hydrant. They are typically made of metal or plastic and can range in size from small diameter pipes to large diameter mains.
- Hoses: Firefighters use hoses to transport water from the hydrant to the site of the fire. They are typically made of rubber or PVC and are available in a variety of lengths and diameters.
- Connectors and Adapters: These are used to connect the hoses to the hydrant and allow for the transfer of water from the hydrant to the hose. They come in different sizes and threads.
- Hydrant Wrench: This is a specialized tool used by firefighters to open the valve on the hydrant.
- Flow meter: It measures the flow rate of the water coming out of the hydrant.
- Alarm and Supervisory Devices: These devices monitor the system and provide an indication of any problems or malfunctions. They can include pressure switches, flow switches, and alarms that alert the fire department to any issues.
A fire hydrant system is an essential component of a community’s fire protection infrastructure and plays a vital role in ensuring public safety by providing a reliable source of water for extinguishing fires.
Color Coding of Fire Hydrants
Fire hydrants are typically painted with a distinctive color scheme, which helps to indicate the available water pressure and the status of the hydrant. The color coding of fire hydrants varies depending on the area, but the most common color codes are:
- Red: indicates low pressure or a dry hydrant. This means that the hydrant is not connected to a water supply or the pressure is too low to be effective.
- Orange: indicates a hydrant that is out of service. This could mean that the hydrant is damaged, is undergoing repairs, or has been taken offline for some other reason.
- Blue: indicates a private hydrant. This means that the hydrant is owned and operated by a private entity, rather than the city or municipality.
- Green: indicates a standpipe. This is a type of hydrant that is connected to a standpipe system, which is typically found in buildings.
- Yellow: indicates a hydrant that is in service and has a high pressure. This means that the hydrant is fully operational and can provide a reliable source of water for extinguishing fires.
It’s important to note that color coding of fire hydrant can vary depending on the area or municipality, and it’s always recommended to check with the local fire department for specific codes used in your area.
Fire hydrants are typically located on public streets and are available for use by fire departments in case of emergency. They are usually painted with a distinctive color scheme, which helps to indicate the available water pressure and the status of the hydrant. The most common types of fire hydrants include wet barrel, dry barrel, underground, pillar and dry standpipe hydrant.