Pump priming refers to the initial injection of government funds into an economy in order to stimulate economic activity and promote growth. This can take the form of infrastructure projects, tax cuts, or increased government spending on social welfare programs. The idea behind pump priming is that by injecting money into the economy, it will lead to increased consumer spending and investment, which in turn will create jobs and stimulate economic growth.
This priming can be contrasted with austerity measures, which involve reducing government spending in order to decrease the budget deficit or national debt. This priming is often used during times of economic recession or stagnation, as a way to boost economic growth and create jobs.
It is important to note that, this priming is not a long-term solution for economic growth and stability. It can help to stimulate the economy in the short term, but it can also lead to inflation and a larger national debt if not used carefully.
Reason for Pump Priming
This type priming is often used as a tool to stimulate economic activity during times of recession or stagnation. The primary reason for this is that during a recession, consumer spending and investment tend to decrease, which can lead to a decline in economic growth and job losses. This priming is intended to counteract this by increasing the amount of money in circulation, which can help to boost consumer spending and investment, and in turn, stimulate economic growth and job creation.
Another reason for this priming is to address the problem of under-utilization of resources, particularly during a recession, when many resources such as labor and capital are not being fully utilized. This priming can help to increase demand for goods and services, which in turn can lead to increased production and job creation.
Additionally, This type priming can also be used as a tool to address social welfare issues. For example, government spending on social welfare programs such as education and healthcare can help to improve the well-being of citizens and reduce poverty.
It’s important to keep in mind that, this priming can have its own set of drawbacks, such as inflation and increasing national debt if not used carefully. Therefore, it is generally used as a short-term solution to stimulate the economy and not a long-term solution for sustained economic growth and stability.
When is Pump Priming Required?
This priming is typically used during times of economic recession or stagnation, when consumer spending and investment are low, and economic growth is sluggish. The goal of this type priming is to increase the amount of money in circulation, which can help to stimulate consumer spending, investment, and economic growth.
There are several indicators that can signal the need for pump priming, such as:
- High unemployment: Unemployment tends to increase during a recession, and pump priming can help to create jobs and reduce unemployment.
- Low GDP growth: A decline in GDP growth is often a sign of a sluggish economy and can indicate the need for pump priming.
- Low inflation or deflation: Low or negative inflation can be a sign of weak demand, and pump priming can help to increase demand for goods and services.
- High Debt-to-GDP ratio: High debt-to-GDP ratio is a sign of a weak economy and can be an indication that the government needs to take measures to stimulate the economy.
- Low consumer and business confidence: Low consumer and business confidence can indicate a lack of faith in the economy and can signal the need for government intervention to boost economic activity.
It’s worth noting that, the decision to use pump priming as a policy tool is usually made by the government or central bank, and it’s often used in conjunction with other policy measures such as monetary policy and fiscal policy. The timing and the extent of pump priming also depends on the specific economic conditions of the country and the government’s priorities.
Pump Priming Methods

There are several methods that governments and central banks can use to implement pump priming:
- Fiscal policy: This involves increasing government spending on infrastructure projects, social welfare programs, or tax cuts. The goal is to increase the amount of money in circulation and stimulate consumer spending and investment.
- Monetary policy: This involves lowering interest rates or increasing the money supply. Lowering interest rates can encourage borrowing and spending, and increasing the money supply can also stimulate economic activity.
- Public works programs: This involves the government directly hiring workers to carry out infrastructure projects or public works. This can create jobs and stimulate economic activity.
- Investment in Research and Development: Government can invest in research and development projects to encourage innovation and product development in specific sectors, which in turn can lead to increased economic growth.
- Subsidies and tax incentives: Government can provide subsidies and tax incentives to certain industries or businesses to encourage investment and job creation.
- Quantitative easing: Central banks can use this method to purchase government bonds and other securities in the open market to increase the money supply and stimulate economic activity.
It’s important to note that, the specific method or combination of methods used for pump priming will depend on the specific economic conditions and the government’s priorities. Additionally, the effectiveness of pump priming depends on the timing, extent, and the coordination of the policy measures.
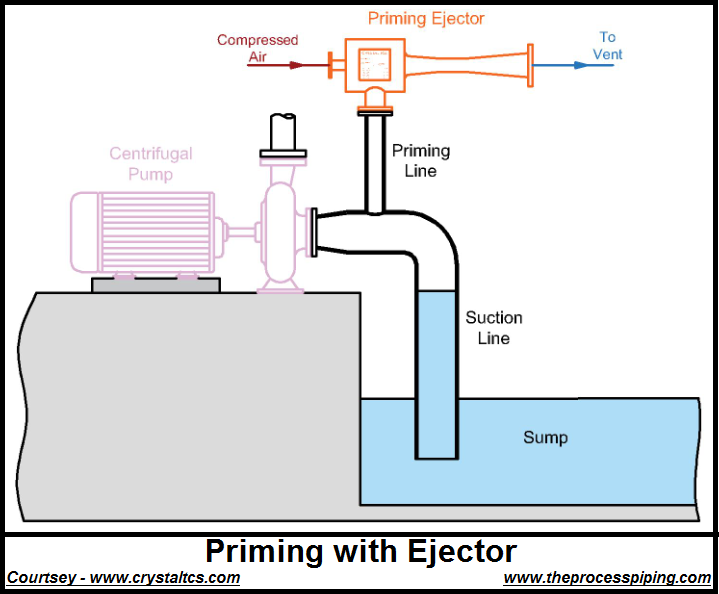
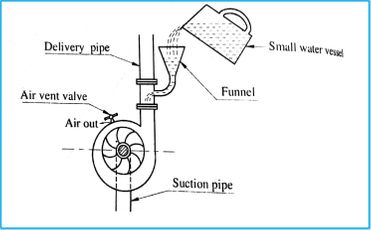
What is a Self-Priming Pump?
A self-priming pump is a type of pump that is able to pump fluid, even if the pump is not submerged in the fluid. This is in contrast to a standard centrifugal pump, which must be fully submerged in order to function.
A self-priming pump is designed to draw air out of the suction line and create a vacuum, then fill the suction line and pump with the liquid. The pump uses a combination of the centrifugal action and the air-water mixture to prime itself and creates a suction lift. The impeller in the pump creates the centrifugal force that throws the liquid out of the pump and the suction pipe is designed to create a vacuum that sucks the liquid into the pump.
Self-priming pumps are used in a wide range of applications where liquid needs to be moved from one location to another, and the pump does not have a constant liquid supply. For example, they are commonly used in irrigation systems, industrial processes, waste water treatment plants, and fire-fighting systems.
It’s worth noting that, self-priming pumps are not suitable for all types of liquid and they generally have a limited suction lift capability compared to other types of pumps. They may require additional components like foot valves or check valves to prevent backflow, and also require regular maintenance to keep them running efficiently.
Prevention of Pump Operation
There are several measures that can be taken to prevent a pump from operating without priming:
- Use a foot valve or check valve: These valves are installed in the suction pipe and are designed to prevent backflow and maintain the prime in the pump.
- Use a low-level alarm: This type of alarm is designed to detect when the liquid level in the pump’s suction pipe is too low and will sound an alarm or shut off the pump before it can operate without a prime.
- Use a level control switch: This type of switch is designed to shut off the pump if the liquid level in the suction pipe is too low.
- Use a dry-run protection system: A dry-run protection system is an electronic device that continuously monitors the flow and pressure of the pump and will shut off the pump if it detects that the flow is too low or the pressure is too high, indicating that the pump is running without a prime.
- Maintaining and monitoring the pump regularly: Regularly inspecting, cleaning, and maintaining the pump can help to prevent it from operating without a prime. This includes checking the suction and discharge lines, checking for leaks or blockages, and ensuring that the pump is properly lubricated.
It’s important to note that, these measures are not foolproof and can’t guarantee 100% prevention of pump operation without priming. However, they can significantly reduce the risk of pump operation without priming, and also helps to detect the problem early, before it causes damage to the pump or system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pump Priming
Advantages of pump priming:
- Stimulates economic growth: Pump priming can increase the amount of money in circulation, which can lead to increased consumer spending and investment, which in turn can stimulate economic growth and job creation.
- Reduces unemployment: Pump priming can help to create jobs and reduce unemployment during a recession.
- Addresses under-utilization of resources: Pump priming can increase demand for goods and services, which can lead to increased production and job creation.
- Addresses social welfare issues: Government spending on social welfare programs can improve the well-being of citizens and reduce poverty.
- Short-term solution: Pump priming can provide a short-term boost to the economy during a recession, helping to stabilize the economy until it recovers on its own.
Disadvantages of pump priming:
- Can lead to inflation: Pump priming can increase the amount of money in circulation, which can lead to inflation if not used carefully.
- Can increase national debt: Pump priming can increase government spending, which can lead to a higher national debt if not financed properly.
- Not a long-term solution: Pump priming is not a long-term solution for sustained economic growth and stability, and should be used in conjunction with other policy measures.
- Can lead to government intervention in the economy: Pump priming can lead to government intervention in the economy which can have negative effects on the private sector.
- Complexity in implementation: Implementing pump priming can be complex, and it’s important that the government carefully considers the timing, extent, and coordination of the policy measures.
It’s important to note that, the decision to use pump priming as a policy tool should be made after careful consideration of the specific economic conditions and the government’s priorities, and it should be used in conjunction with other policy measures.